- About
-
Treatments
- Infertility Counselling
- Ultrasound Monitoring
- Intrauterine Insemination
- IVF Treatment
- ICSI
- Blastocyst Transfer
- Laser-Assisted Hatching
- EmbryoGlue
- Genetic Testing Of Embryos
- Personalized Embryo Transfer
- Frozen Embryo Program
- Donor Services
- Fertility Preservation
- Egg Freezing
- Male Infertility Treatments
- Management of Recurrent IVF failures
- Surrogacy
- Patients
- Gallery
- Blog
- Contact
What is embryo preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) in IVF ?
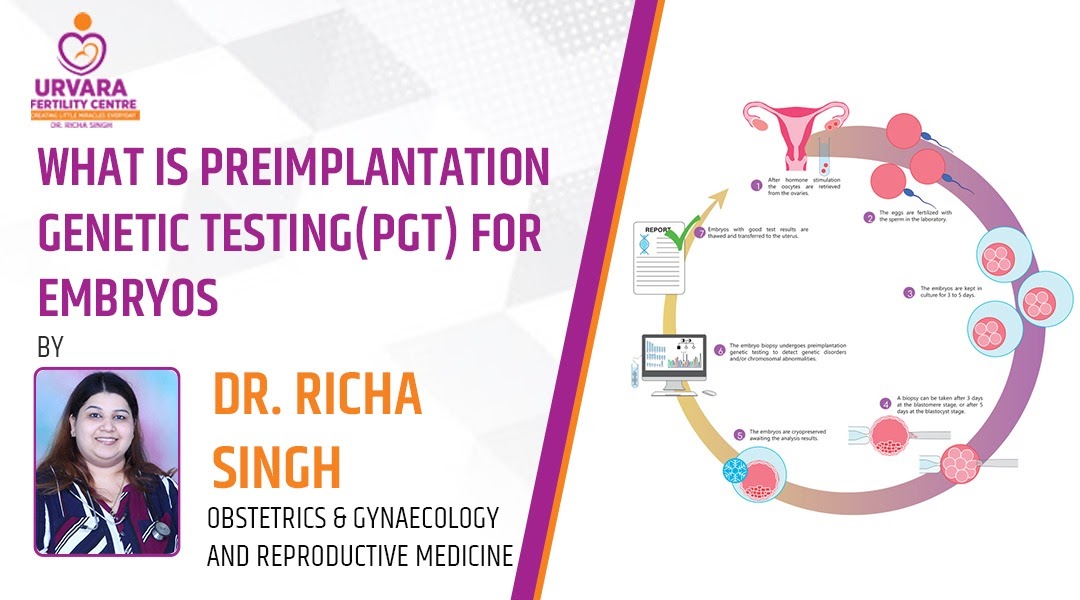
What is embryo preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) in IVF ?
Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) checks embryos during in vitro fertilisation (IVF) before probable transfer to a woman's uterus for a variety of genetic issues that can result in implantation failure, miscarriage, and birth abnormalities in the ensuing child. For the best chances of success in this treatment one should take appointment for infertility doctor Dr. Richa Singh who is the best infertility doctor in Lucknow for PGT testing.
A missing or extra chromosome in the embryo (for example, Down syndrome), single gene diseases (such as sickle cell anaemia), or gene rearrangement can all result in pregnancy loss and birth abnormalities.
There term PGT is a new word that encompasses the same tests as the previously titled and more well-known as preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) and preimplantation genetic screening (PGS).Embryologists utilise PGT testing during IVF to detect genetic flaws in embryos so that only those embryos which are genetically healthy are transplanted to the woman's uterus to achieve conception.
Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) encompasses three types of tests that can be conducted on embryos during IVF:
Preimplantation genetic screening for chromosomal abnormalities (PGT-A)
preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic diseases PGT-M)
PGT For known chromosomal mis-arrangements such as inversion and translocation known as preimplantation genetic testing structural rearrangement (PGT-SR)
Fertility doctors perform these tests for two reasons. One is to see if the embryos have genetic abnormalities, which frequently result in failure of implantation and miscarriage, resulting in failed IVF or failed pregnancy .
PGT testing is also used to enhance the chances of success in ivf treatment.
The testing is also used to identify embryos with hereditary genetic disorders like monogenic diseases that could result in a child with a genetic abnormality or inheritable disorders like muscular dystrophy ,sickle cell anemia ,thalassemia ,haemophilia and many more .
So through PGT one can find out which ones are the unhealthy embryos and Embryos with such faults are not allowed to be transferred to the mother's womb for a pregnancy.
According to research, genetic defects in embryos are a primary cause of unsuccessful pregnancy.Couples interested in PGT testing can meet with a fertility specialist specialised in this to discuss potential options.Lets know more about these tests .
1- Aneuploidy testing in preimplantation genetics (PGT-A)
PGT-A is a test that looks at embryo cells to see if they have the proper number of chromosomes. An embryo with too few or too many chromosomes might emerge from uneven division of sperm or egg cells.Because individuals inherit 23 chromosomes from each parent, most people have 46 chromosomes. Aneuploidy occurs when an embryo or cell lacks or possesses an extra chromosome. A missing chromosome is referred to as monosomy, and an extra chromosome is referred to as trisomy.
Turner syndrome, which is the lack of one of the X chromosomes, is the only type of monosomy that a kid can survive. Trisomy of chromosome pairs, commonly known as trisomy 21 or Down’s syndrome (an extra chromosome in normal pair at 21),Edward syndrome (trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome of trisomy 13) .According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, one in every 700 newborns is born with Down syndrome.Aneuploidy is a primary cause of pregnancy failure and miscarriage, as well as a major source of birth abnormalities in children.
2- Genetic testing for a monogenic illness during preimplantation (PGT-M)
PGT-M looks for specific gene mutations that one (or both) of the parents has. A family history of genetic abnormalities in one or both parents increases the likelihood that a child would be born with a genetic mutation.A mutation in the DNA sequence causes a disease involving a particular specific gene. This causes disorders including cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anaemia. It can also result in an inherited genetic mutation, such as the BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, which raise a woman's risk of breast and ovarian cancer significantly.
During PGT-M, the fertility specialist will screen the embryos for certain genetic diseases before transferring the embryo to the woman's uterus. For detailed information one can book appointment with the top ivf centre in lucknow.
PGT-M investigates prevalent illnesses such as:
PGT-SR examines embryos from patients who have been diagnosed with a chromosomal structural rearrangement, such as an inversion or translocation. Patients who have a known structural rearrangement are more likely to produce embryos with an insufficient amount of chromosomal material. The afflicted embryos have a lower chance of resulting in a live baby. Miscarriages are common in patients with these issues.
PGT-SR investigates illnesses such as:
During IVF, how are PGT-A, PGT-SR, and PGT-M conducted on embryos?
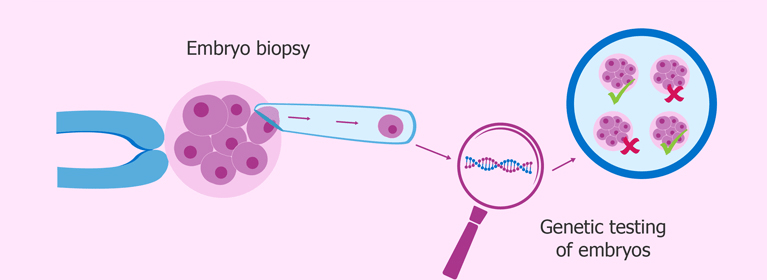
The first and second phases in all three forms of PGT are the same. An embryo biopsy is the initial step. The biopsy is then analysed by a laboratory to undertake genetic testing on DNA.
The biopsy is taken at the blastocyst stage of development (day 5 or day 6 of embryo culture) in both types of testing. The blastocyst is made up of two cell types: trophectoderm (TE), which permits the placenta to form, and inner cell mass (ICM), which eventually develops into the baby.
The biopsy extracts 5-8 cells from the trophectoderm (pre-placenta) for testing for genetic abnormalities in the laboratory. The cells that will give birth to the foetus are not disturbed. Typically, results are available 7-10 days after the biopsy. After being biopsied, the blastocyst is stored to await the results of the testing before being thawed and transferred to the woman in a subsequent cycle.
Mosaicism in embryos can now be detected using NGS (next generation sequencing).
The embryo biopsy is tested in the laboratory using next generation sequencing (NGS), which employs molecular analysis and advanced computation to detect the possibility of chromosomal abnormalities. Until recently, NGS data were simply considered aberrant or normal, providing a good or unfavourable embryo rating.
However, there is a grey space in between those absolutes known as mosaicism. NGS can now identify mosaic embryos with varying proportions of defective and normal cells. A blastocyst embryo has more than 100 cells, and in a mosaic embryo, some are defective and some are normal. A high-level mosaic embryo will have a majority of defective cells and only a few normal cells. A low-level mosaic will consist primarily of normal cells.
Previously, preimplantation genetic testing was incapable of detecting mosaicism. NGS can now pinpoint the extent of mosaicism, providing physicians and patients with a more comprehensive study that can boost the likelihood of a successful pregnancy and birth. Book your appointment with best ivf specialist for your treatment.
Share Now
.png)